Renewable solutions
5 minute read
How are renewable fuels produced?
Why do we need renewable fuels? What are they made of? And do we have enough renewable raw materials to produce them?
In order to significantly reduce greenhouse emissions that accelerate climate change, we must harness all solutions to replace those currently made from fossil resources. We cannot continue depleting fossil resources and releasing additional carbon into the atmosphere. Instead, we should reuse and recycle already existing materials, and whenever we need new resources, we must focus on those that are renewable.
Where should renewable fuels be used?
Sales of electric vehicles are accelerating, and hydrogen is taking its first steps. The composition of the vehicle fleet is changing, but a more comprehensive shift will take time. The majority of vehicles, especially heavy goods vehicles, will still rely on internal combustion engines in 2030 and beyond. Therefore, we need a solution to reduce the emissions of these existing vehicles today and in the future.
Renewable fuels can be adopted by all modes of transport on the roads, in the skies and in the seas. Not only cars, vans, trucks, planes and ships can all run on renewable fuels, but also heavy-duty machinery, such as cranes, excavators and loaders, can be operated using renewable fuels. By using renewable fuels, such as Neste MY Renewable Diesel™, greenhouse gas emissions can be reduced by as much as 75 to 95%* over the fuel’s life cycle when compared to fossil diesel.
Neste’s renewable fuels can be used in existing vehicles, planes and ships. This will allow these fuels to be adopted quickly.

What are renewable fuels made of?
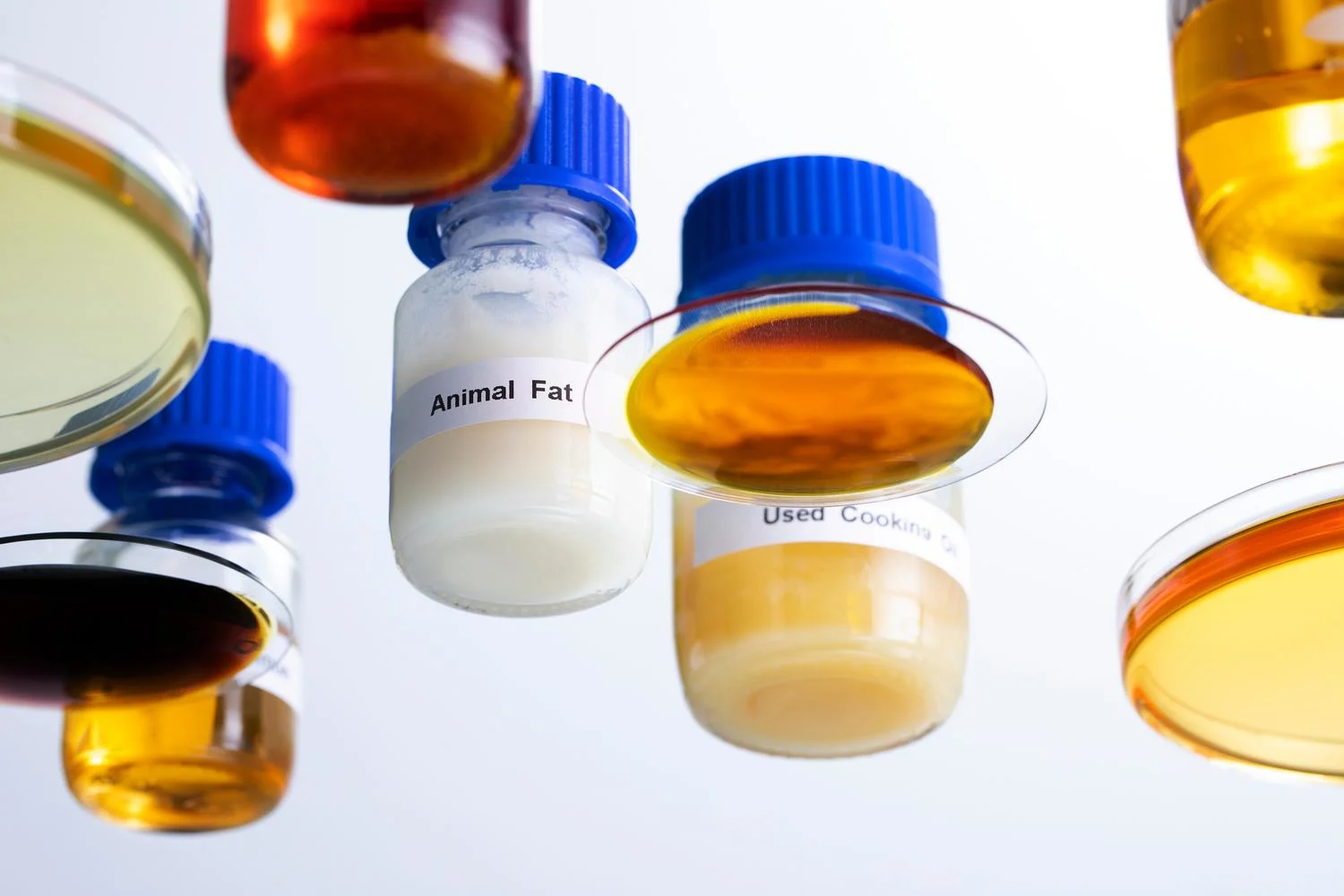
The main difference between renewable fuels and fossil fuels is where they come from. Fossil fuels are made from non-renewable fossil resources, such as crude oil, and their use releases the carbon from these fuels into the atmosphere. Renewable fuels are made from renewable raw materials such as waste and residues or from oil extracted from plants that absorb CO2 from the air through photosynthesis.
Neste uses an extensive portfolio of renewable raw materials, including used cooking oil, animal fat waste and vegetable oil processing waste and residues. The company has focused on waste and residues for over a decade, and they now represent more than 90% of Neste’s global renewable raw material inputs. We expect to use also other types of raw materials besides waste and residues in the mid and longer term, such as algae or novel vegetable oils produced with regenerative farming practices. Neste is also researching the potential of CO2 absorbing algae and using CO2 itself as a raw material.
Sustainability guides Neste’s global sourcing of raw materials. Optimized sourcing and logistics ensure an efficient and continuous flow of raw materials for our refineries in Finland, the Netherlands and Singapore and for our joint operation in Martinez, California.
Most materials need to be pretreated to remove impurities. The specific pre-treatment carried out depends on the type of raw materials. After the pretreatment, raw materials are refined into a variety of renewable products using Neste’s NEXBTL process. The unique NEXBTL technology is the result of years of research and innovation. The combination of pretreatment and the NEXBTL process ensures that a diverse set of raw materials, even lower quality waste and residues, are turned into renewable products with consistently high quality.
The raw material inputs in our refining may vary over time, from market to market and from product to product, based on availability, price, the market and customer-specific requirements and preferences. Neste’s extensive raw material portfolio provides us with flexibility to meet these requirements.
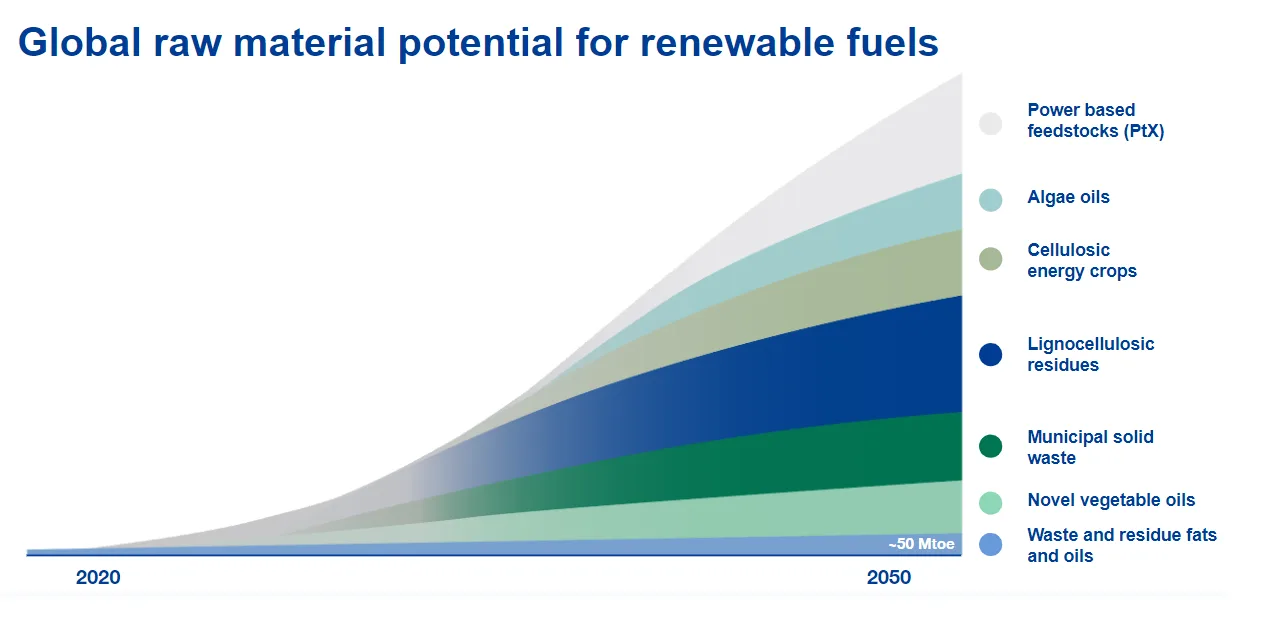
Do we have enough renewable raw materials?
By 2040, a range of new renewable raw materials and processes could allow global renewable fuel production to grow substantially, reaching over 1,000 megatons of oil equivalent. Today, global energy demand for transport is 2,668 megatons of oil equivalent across all modes of transport. By broadening the raw materials base, renewable fuels could replace all fossil aviation and marine fuels, and substitute a substantial amount of fossil fuels in road transport by 2040.
Multiple raw materials can replace fossil raw materials in the fuel production. Some are available already today, and with innovation we can unlock the future potential of many others. Regulators hold the key to ensuring the eligibility of a broad raw material pool to enable the full emission reduction potential of these renewable raw materials.
Neste continues to work towards increasing the availability of renewable and recycled raw materials, while also developing technologies to diversify our current raw material portfolio even further from what it is today. This will help us ensure access to sufficient volumes of raw materials to support our growing production capacity.
Neste currently produces approximately 3.3 million tons of renewable products annually. Neste’s Singapore refinery expansion and the joint operation, Martinez Renewables, with Marathon Petroleum in Martinez, California, will increase Neste’s total production capacity of renewable products to 5.5 million tons by the beginning of 2024.
As the global leader in renewable diesel and sustainable aviation fuel, as well as a forerunner in the field of renewable and circular solutions for the polymers and chemicals industry, Neste empowers its customers to switch to more sustainable solutions, today.
*) The GHG emission reduction percentage varies depending on the region-specific legislation that provides the methodology for the calculations (e.g. EU RED II 2018/2001/EU for Europe and US California LCFS for the US), and the raw material mix used to manufacture the product for each market.
Credits:
Neste




